3.6 Object
An object is a materialization (instance) of a class. The parts that make up the screen (buttons, windows, etc.), the characters to be printed, and the elements of the data to be processed are all managed as objects.
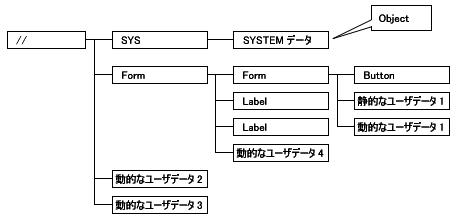
Hierarchical structure of objects
Biz / Browser manages objects in a hierarchical structure with the object named “//” ( Root object) as the vertex. Most objects are included in this hierarchy. The Root object is the base point of the hierarchical structure and is the object corresponding to the Biz / Browser window that exists only once .
There is always a “ SYS object “ (system data) as a child object of the Root object, and there are other objects that represent screens and data defined by the application.
There are also temporary objects that do not belong to the hierarchical structure that is based on “//” ( Root object).
All objects are maintained by reference relationships and are not deleted while one object is referenced by another. Objects connected to a hierarchical structure based on “//” ( Root object) always refer to child objects from the parent object, so unless you explicitly break the parent-child reference relationship. Will be maintained.
Objects that are no longer referenced from anywhere are temporarily stored in memory, but are collected and released by the garbage collector of the CRS interpreter.
Project Type
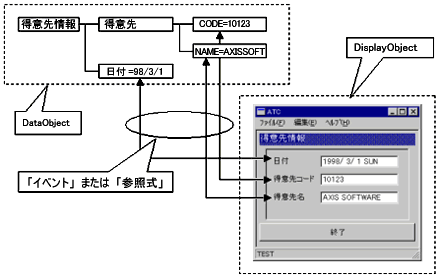
Biz / Browser has many built-in classes. Classes can be roughly divided into display classes (hereinafter DisplayObject ) derived from the DisplayObject class and other data classes (hereinafter DataObject ).
DataObject is a basic class for managing the value of data, and the data processed by the application can be managed with a logical hierarchical structure, and it is maintained in the data communication between the client and the server or in the client. It can be used as a temporary work area.
In addition to the functions of data-based objects, DisplayObject is displayed on the screen or form with the same overlap as the hierarchical structure of objects. These objects provide the user with an interface for displaying information and entering data.
DisplayObjects and DataObjects can propagate data to each other in the following ways:
- The “event handler” defined in the object captures and processes the “event” that occurs as a result of screen operations by the user.
- Set automatic recalculation by “reference operator ( & = )” that represents the relationship between objects .